Introduction
The quadratic model is a very common model used in physical science
and mathematics and often is associated with motion or distance and time.
If a ball is thrown into the air a quadratic function would best describe
the distance of the ball from a fixed horizontal position with respect
to time.
The quadratic function is a function of the form: 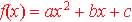 ,
where a, c, and c are constants. ,
where a, c, and c are constants.
The height, h(t) of a ball in feet from the top of a tree thrown vertical
with respect with time, t in second. may be a quadratic model shown by
the formula 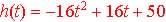 . .
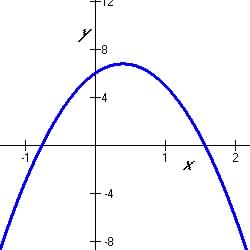
The graphs of quadratic function have symmetrically characteristic shapes
that looks like the Figures below:
Table 5.5.1 Optima of Quadratic Functions
| Figure
5.5.1 Quadratic Maximum
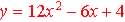
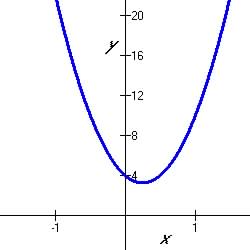
|
Figure
5.5.2 Quadratic Minimum
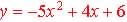
|
A quadratic function is also a polynomial and like polynomials the zeros
of the function helps define many characteristics for the model.
There are three forms for the quadratic function that is presented in
this text:
1. The Standard form: 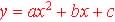 ,
where a, b, and c are constants ,
where a, b, and c are constants
Example 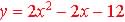
2. Vertex Form: 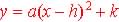 ,
where a is a constant and (h, k) is the coordinate
of the vertex ,
where a is a constant and (h, k) is the coordinate
of the vertex
Example 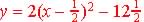 ,
where the vertex or the minimum of the function is at ,
where the vertex or the minimum of the function is at
( ½ , 12 ½ )
3. The Zero Form: 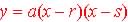 ,
where a, r and s are constants ,
where a, r and s are constants
Example 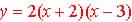 ,
and the graphs crosses the x-axis at x = -2 and x = 3 ,
and the graphs crosses the x-axis at x = -2 and x = 3
So 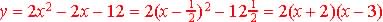
Table 5.5.2 Graphical Representation of Various Quadratic Functions
| Figure
5.5.3 Quadratic Graphic Equivalency
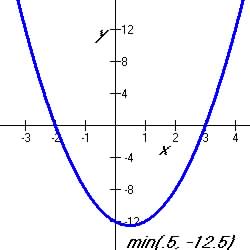
|
Precalculus: Contemporary Models
by Pin D. Ling
|