| Continuous Random Variable - Normal Distribution
An adjusted histogram is
the conversion of a frequency distribution to a probability distribution.
The probability that a continuous random variable assumes
some value in an interval is represented by the area under the portion
of the continuous curve of that interval.
A uniform distribution has the same frequency for each value
of x.
The standard normal random variable is a normal variable with
mean = 0 and standard deviation = 1. Its value is represented by the symbol,
z.
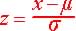 (the data value minus the mean divided by the standard deviation)
(the data value minus the mean divided by the standard deviation)
| The z-score or
z values of a normal variable, x corresponds to the number of standard
deviations of about the mean |
.
Central Limit
Theorem: As samples size, n increases
the sample distribution approaches the normal distribution. (n 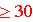 ) ) |
|